Introduction example of optical switch
NTT-AT 's optical switch units have shipped a total of several thousand units, accommodating more than tens of thousands of ports of optical fiber communication equipment, and supporting the business activities of communication carriers, ISPs, and others.
We interviewed an Internet Interconnection (IX) service provider about the process from considering the introduction of the intelligent optical switch unit to its development and operation, the specific effects, and future developments.
(February 2015)
(February 2015)
Application examples of optical switches
Here are some typical application examples of optical switch units.
- IX service L2 switch redundancy
- Redundant points of interconnection with Internet access lines
- Redundancy of ISP transit connection services
- Aggregation router redundancy
- Ring aggregation (LAG) redundancy for inter-DC connections
- Redundancy of transmission lines between remote locations
- High-layer appliance bypass redundancy
- Reduction of human error
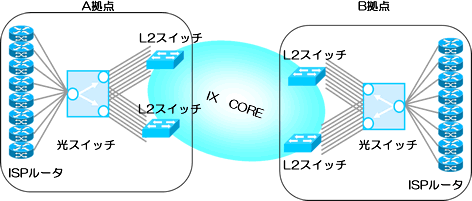
IX service L2 switch redundancy
The single line connecting to the user can be redundant while ensuring the transparency of the optical signal in the event of a failure. Improves reliability at critical points where many circuits are aggregated.
Redundant points of interconnection with Internet access lines
ISP's
- cloud service
- Internet connection service
- Applies to Internet VPN services, etc.

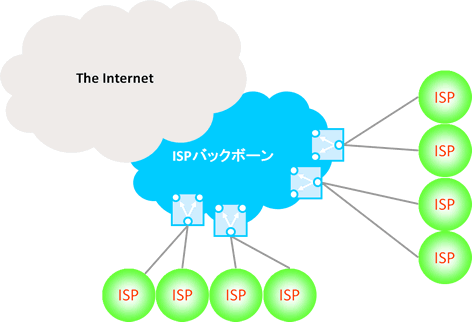
Redundancy of ISP transit connection services
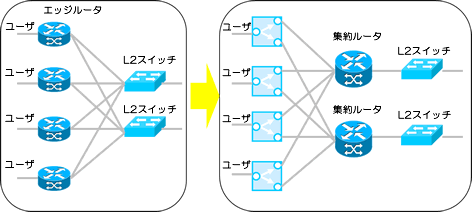
Aggregation router redundancy
Router redundancy and aggregation can be achieved, and the degree of impact in the event of a failure can be reduced.
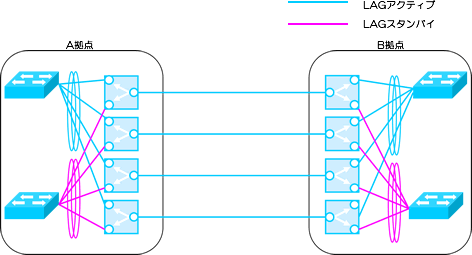
Ring aggregation (LAG) redundancy for inter-DC connections
LAG connection ports between short-distance DCs or between floors can be grouped together for redundancy.
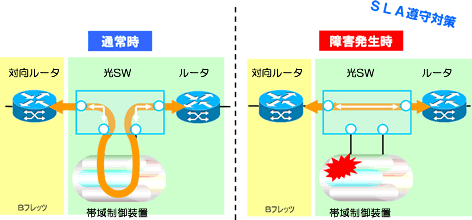
Redundancy of transmission lines between remote locations
Redundant transmission path beyond CWDM/DWDM. By using NSW as a stand-alone, two-way carrier diversity can be achieved.
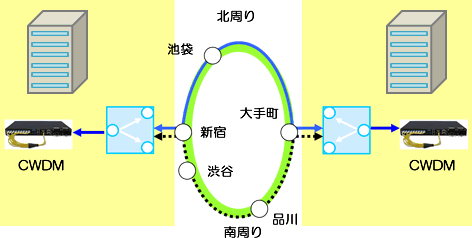
1+N redundant configuration example
One backup transmission line can be shared with N current transmission lines.
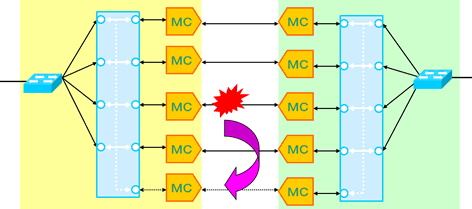
High-layer appliance bypass redundancy
In the event of a failure in a connected appliance (bandwidth control device, F/W, etc.), the appliance is instantly disconnected to minimize the impact on the entire network.
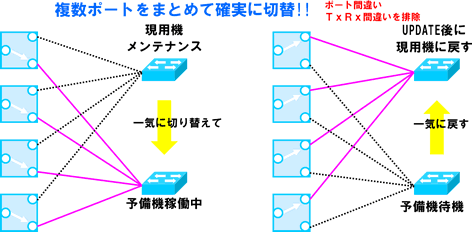
Reduced human error (benefits other than redundancy)
Reduces human error during equipment renewal and maintenance.
You can work without mistakes when there are many ports, such as when LAG is formed with multiple ports.


 close up
close up