Will there be radio interference when spring approaches?
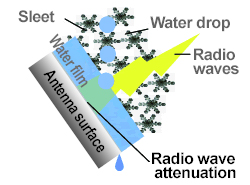
Snow and sleet during the melting season contain a lot of water.
Snow containing a lot of water adheres to the surface of the antenna., when a thick water film occurs, a large amount of radio wave attenuation occurs.
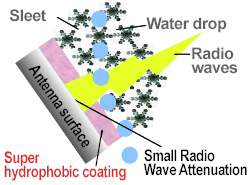
When the antenna surface is treated with Super hydrophobic...
Radio wave attenuation can be reduced compared to when a Super hydrophobic film is formed without water repellent treatment.
The figure below shows the calculated radio wave attenuation when a thick water film (0.5 mm, 1.0 mm) is formed due to the large amount of water retained in the snow during sleet.
As can be seen from the figure, even in the low-frequency range, where the effect of the water film is not so great, attenuation that does not occur in normal rain occurs when the water film becomes thicker.
When the snow melts, it is the same as when it is sleet. Attenuation occurs when a thick water film is formed.
(supplement)
Radio wave attenuation due to ice is very small compared to water. Since snow is a mixture of ice and air, snow attenuation is less than ice attenuation.
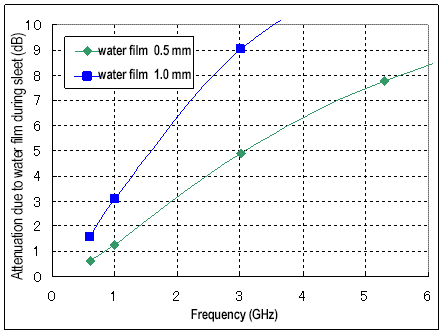
*Data below 3GHz were calculated using the refractive index and absorption rate of water at 3GHz, assuming the temperature to be 0°C.


 close up
close up